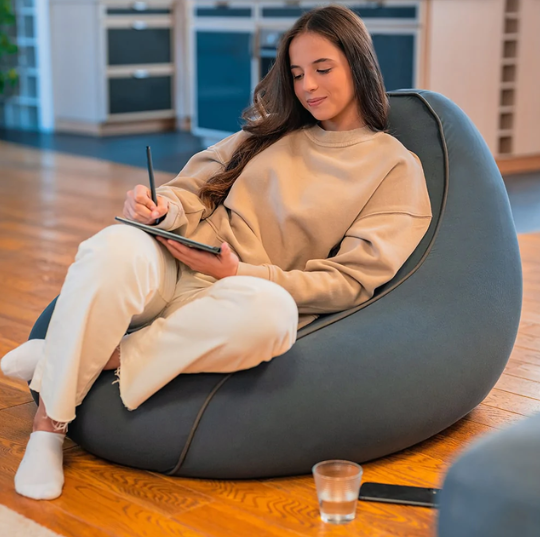
Incorporating the Yogibo Vibroacoustic Chair into educational settings is not just a theory for me; it’s a concept I’ve experienced firsthand and seen its impact. Although my encounter was with a Vibro bed, a cousin to the Yogibo Chair in technology, the essence of vibroacoustic therapy (VAT) remained the same.
My experience
I remember the first time I lay on the Vibro bed. The world around me seemed to fade away as the low-frequency sound vibrations began to work their magic. It was more than just physical relaxation; it was as if each wave of sound was washing away the stress and noise of everyday life. I emerged from the experience feeling rejuvenated, with a sense of calm that I hadn’t felt in a long time. It was a stark reminder of how powerful this technology can alleviate stress and promote mental well-being.
This technology’s impact extended beyond my own experience. I recall a young child with mild Asperger’s Syndrome who used a similar technology. The transformation was remarkable. According to his parents, not only did he find immense joy in the sensory experience, but they also noticed a significant improvement in his behaviour and abilities at home. It was as if the therapy had unlocked a new level of potential in him, helping him to navigate his world with greater ease and confidence.
These experiences, though with a different product, underscore the potential of the Yogibo Vibroacoustic Chair in educational environments. They are vivid reminders that this technology isn’t just about creating a unique learning tool; it’s about touching lives, easing burdens, and opening new doors of possibility for students, especially those with special needs.
At School
Incorporating VAT through the Yogibo Chair in schools could be a transformative step, bringing the same sense of peace, relaxation, and potential for growth that others and I have experienced. It’s a testament to the profound impact that holistic approaches can have in nurturing not just the intellectual but also the emotional and sensory well-being of students and educators alike.
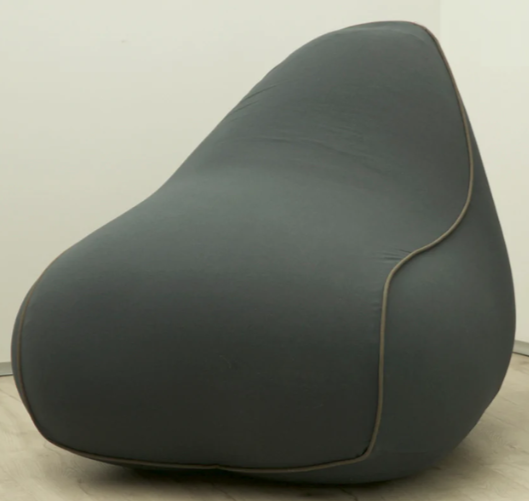

It’s particularly beneficial for enhancing cognitive readiness and supporting students with sensory processing disorders, Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). The chair also contributes to an inclusive learning environment, enriches creative education, and serves as a stress management tool for educators.
Overall, the incorporation of the Yogibo Chair in schools aligns with holistic educational approaches, focusing on the overall well-being of pupils and educators. This approach enriches the learning experience, catering to a wide range of needs.
Further reading
For a more detailed overview of the therapeutic applications and benefits of VAT, refer to the following studies: “Effects of vibroacoustic music on challenging behavior in individuals with autism and development disabilities” by Lars-Olov Lundqvist, Gunilla Andersson & Jane Voding “Vibroacoustic Therapy: Sound Vibrations in Medicine,” and “Contemporary Vibroacoustic Therapy Perspectives on Clinical Practice, Research, and Training,”.
BACK